<h4>Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR – Near Surface Applications</h4>
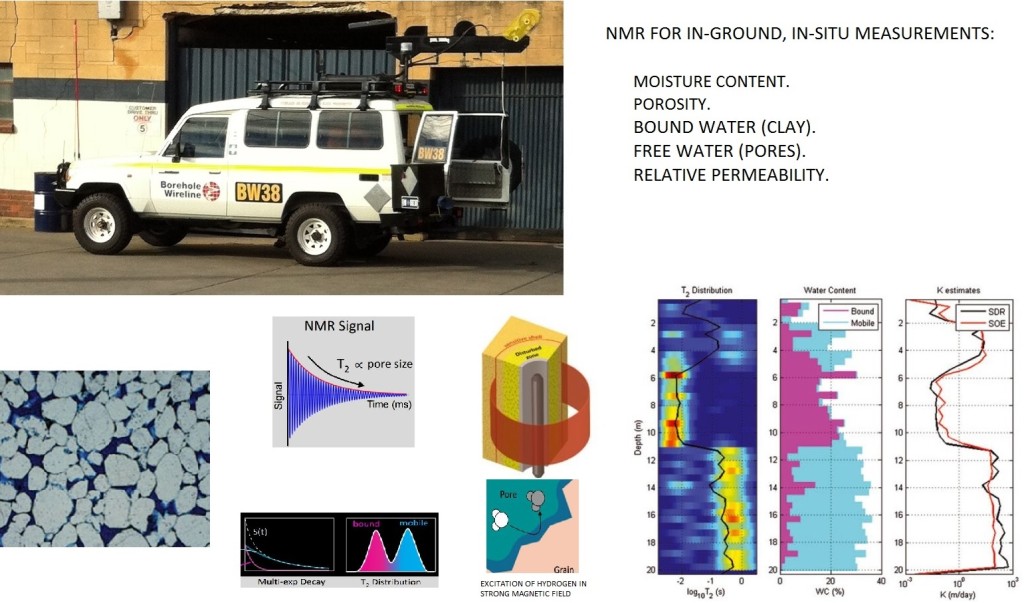
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) borehole logging technique has been developed for near surface mining, groundwater and environmental contamination projects. The NMR technique provides a direct and unambiguous measurement of groundwater. With a direct view into the pore space, NMR data enables precise quantification of moisture content and porosity of the rock surrounding a borehole. Additional parameters measured include an estimation of other critical hydrogeological parameters such as permeability, specific yield and pore size distribution.
<h4>The logging technique</h4>
The NMR logging technique is a magnetic technique and does not require a radioactive source. This allows the NMR logging technique to replace the conventional neutron logging for moisture content and porosity. The NMR logging technique has the ability to distinguish between bound water in clays and free water in the pores allowing the identification of clay/shale layers in the sub surface and support interpretation for conventional logs such as resistivity and gamma.
<h4>The Vista Clara Javelin system</h4>
The Vista Clara Javelin NMR logging system is designed specifically for near surface applications. A range of different probes are available to suit the casing and drilled diameter. The objective of the different probe size is to take measurements beyond the disturbed zone created during the drilling of the borehole. The system includes adaptive noise filters to get over potential near surface environmental noise, such as overhead power lines, which could affect the NMR data.
<h4>Applications</h4>
Some examples of the potential applications of the NMR are technology:
- Measuring the moisture content of the “vadose zone” above the water table. More environmental contamination projects are beginning to show the importance of the moisture content controlling the migration pathways of certain contaminants.
- As the NMR technology is able to distinguish between water bound into the structure of clays (hence unavailable for extraction) and water present in the pore space (hence potentially available for extraction), it will have great significance in the placement of screens in monitoring and/or production bores.
- Many environmental contaminants at the present day are hydrocarbon based. The NMR technology detects hydrogen in water or hydrocarbons.